Our free credit score service has moved
Our free credit score service is now only available through the CommBank app.
If you already have the CommBank app (IOS or Android) installed, simply log into the app, search ‘check credit score’ and follow the on-screen prompts.
Not a CommBank customer? No problem.
You can download the CommBank app and access your Experian credit score for free without needing to have a CommBank financial product. Just make sure you have one form of physical ID handy to verify you are who you say you are. Open the app and once the heading ‘Get started’ appears, select ‘Check your credit score’, then follow the on-screen prompts.
For more information about accessing our free credit score service in the CommBank app, visit our FAQs.
Download the CommBank app

Help others to unlock their full financial potential.
Are you looking at ways to improve the financial well-being of your customers or team? If so, we’d love to hear from you
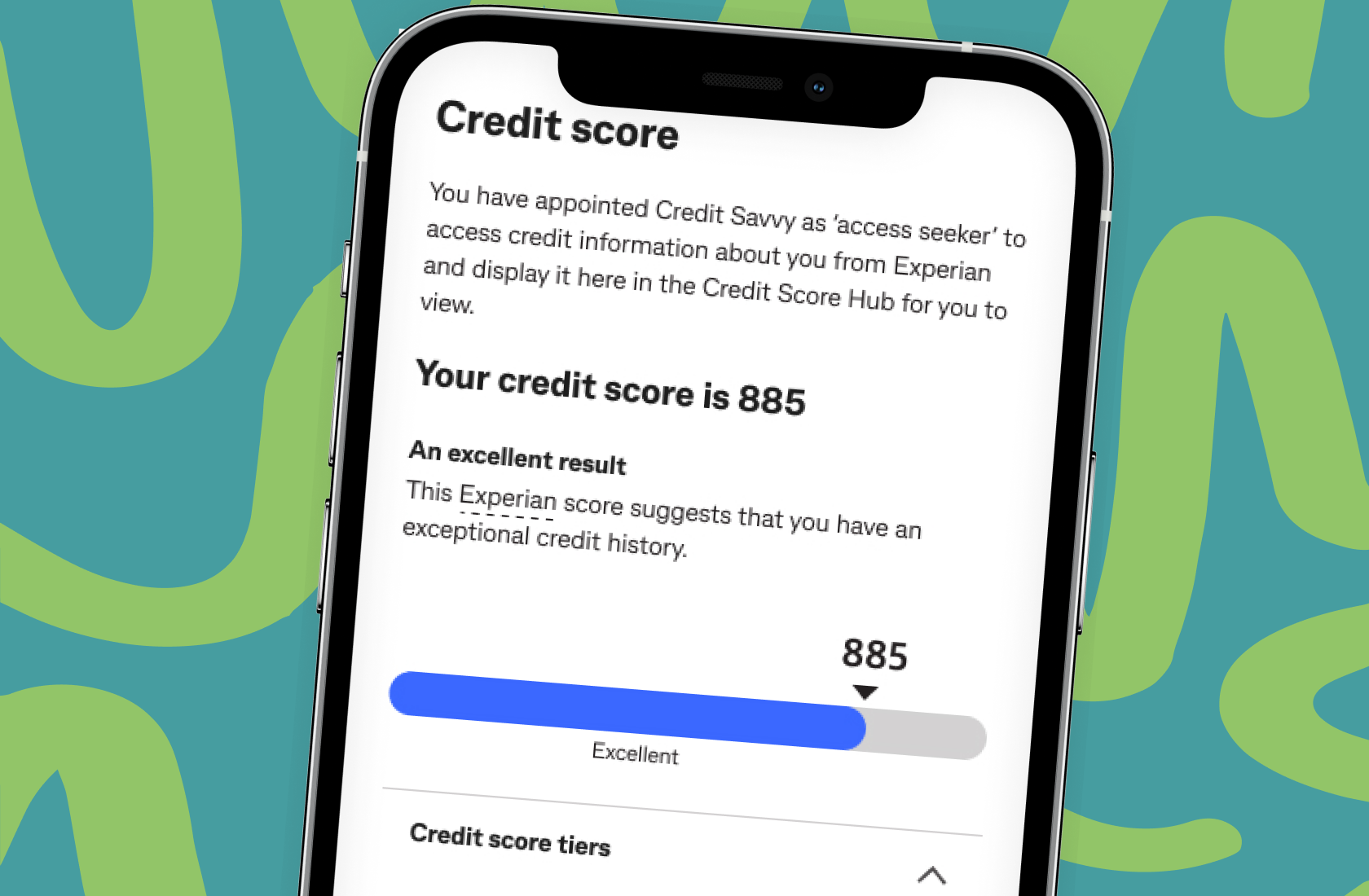
Find out more about our free credit score service inside the CommBank app.
Since 2022, millions of people have chosen to access their credit score with us, conveniently and for free, through CommBank’s award-winning app. Keen to see what we’re all about? Take a look. You won’t even need to hold a CommBank financial product to sign-up.
Testimonials from our customers

Credit Savvy has become a trusted partner in delivering value to our customers. Their credit score reporting not only enhance our mobile app’s functionality but also drives deeper engagement by empowering customers to take control of their financial futures. We’re impressed by their reliability of the service and look forward to growing this partnership.
Joel
CBA - Consumer Finance, April 2025

Credit Savvy’s solution has been a game-changer for our customers. Their seamless API and access to insightful credit reporting from Experian helps our customers understand their credit health in detail, helping them make better financial decisions. The Credit Savvy team is incredibly responsive, making collaboration effortless. I highly recommend their service.
Max
CBA - Consumer Finance, April 2025

